Synthesis, Characterization, and Photocatalytic Application of ZnO@Gelatin Nanocomposite Derived from Chicken Feet for Methylene Blue Degradation
الكلمات المفتاحية:
Gelatin، Chicken feet، Photodegradation، ZnO@Gelatin nanocompositeالملخص
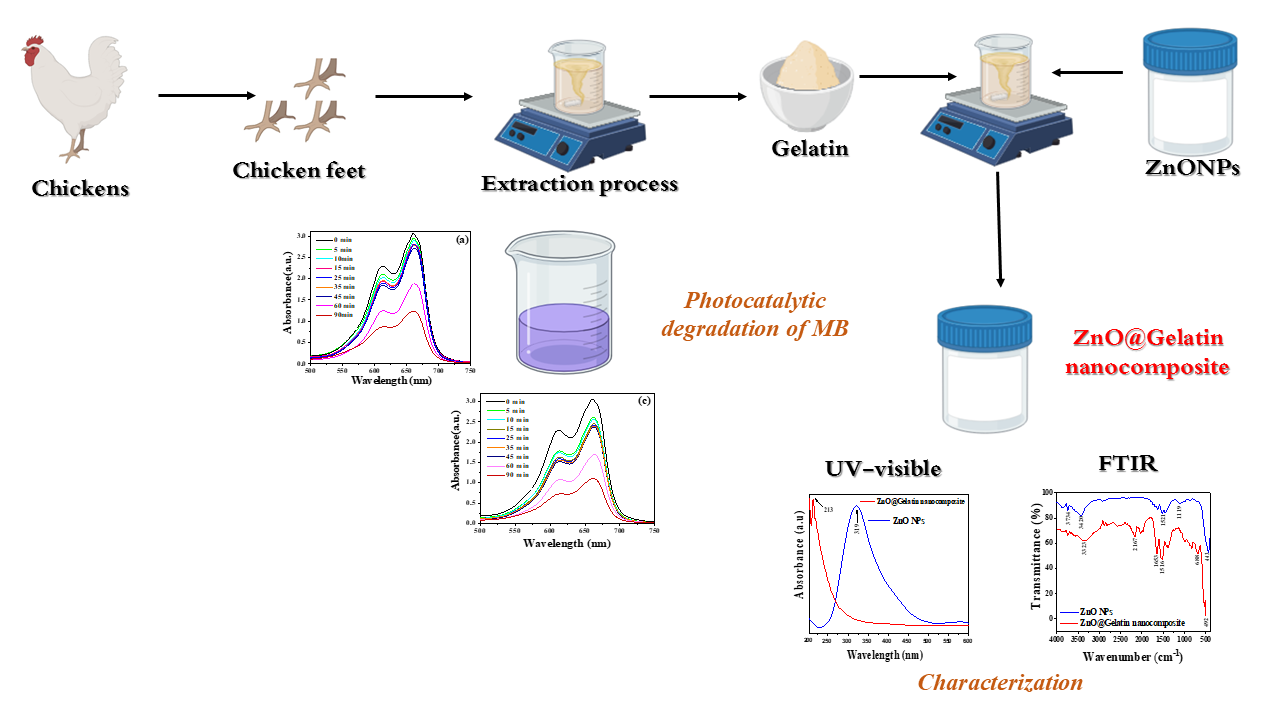
This study explores the synthesis and photocatalytic performance of a ZnO@Gelatin nanocomposite made from chicken foot gelatin, a sustainable by-product. The nanocomposite was characterized for its physicochemical properties and analyzed using FTIR and UV-Vis spectroscopy. It achieved 85% methylene blue (MB) degradation under UV light in 90 min, surpassing ZnO nanoparticles (75%). Gelatin’s functional groups improved dye adsorption and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, with confirmed stability and reusability. This work offers an eco-friendly approach to using chicken foot waste for effective wastewater treatment.
التنزيلات
المراجع
[1] S. J. P. J. o. S. Shah, "Impact of industrial pollution on our society," vol. 73, no. 1, 2021.
[2] I. Khan et al., "Review on methylene blue: its properties, uses, toxicity and photodegradation," vol. 14, no. 2, p. 242, 2022.
[3] A. Kassa, A. Engida, M. J. D. Endaye, and W. Treatment, "Eco-friendly adsorbents for industrial dye removal: A comprehensive review of low-cost alternatives," vol. 323, p. 101362, 2025.
[4] V. Katheresan, J. Kansedo, and S. Y. J. J. o. e. c. e. Lau, "Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review," vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 4676-4697, 2018.
[5] C. Sushma and S. J. C. P. Girish Kumar, "Advancements in the zinc oxide nanomaterials for efficient photocatalysis," vol. 71, no. 10, pp. 2023-2042, 2017.
[6] P. Uikey, K. J. I. J. o. E. T. i. C. S. Vishwakarma, and Electronics, "Review of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles applications and properties," vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 239-242, 2016.
[7] E. Sohouli et al., "Application of polysaccharide-based biopolymers as supports in photocatalytic treatment of water and wastewater: a review," vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 3789-3809, 2022.
[8] R. F. Herin et al., "Functionalized ZnO NPs and biopolymers-coated ZnO NPs for drug delivery and biomedical applications—a review," vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 165-189, 2025.
[9] M. A. Elgadir and A. A. J. F. Mariod, "Gelatin and chitosan as meat by-products and their recent applications," vol. 12, no. 1, p. 60, 2022.
[10] A. Wawrzyńczak, J. Chudzińska, and A. J. C. Feliczak‐Guzik, "Metal and metal oxides nanoparticles as nanofillers for biodegradable polymers," vol. 25, no. 10, p. e202300823, 2024.
[11] O. Aidat, L. Belkacemi, M. Belalia, and M. J. I. F. R. J. Zainol, "Optimisation of gelatine extraction from chicken feet-heads blend using Taguchi design and response surface methodology," vol. 30, no. 5, 2023.
[12] Z. Tabassum et al., "Recent trends in nanocomposite packaging films utilising waste generated biopolymers: Industrial symbiosis and its implication in sustainability," vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 127-153, 2023.
[13] A. Tripathi et al., "Substantial utilization of food wastes for existence of nanocomposite polymers in sustainable development: a review," vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 24727-24753, 2024.
[14] O. Aidat, L. Belkacemi, M. Belalia, M. khairi Zainol, H. S. J. I. J. o. G. Barhoum, and F. Science, "Physicochemical, rheological, and textural properties of gelatin extracted from chicken by-products (feet-heads) blend and application," vol. 32, p. 100708, 2023.
[15] P. Makuła, M. Pacia, and W. Macyk, "How to correctly determine the band gap energy of modified semiconductor photocatalysts based on UV–Vis spectra," vol. 9, ed: ACS Publications, 2018, pp. 6814-6817.
[16] X. Chen, Z. Wu, D. Liu, and Z. Gao, "Preparation of ZnO photocatalyst for the efficient and rapid photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes," Nanoscale research letters, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1-10, 2017.
[17] P. S. Pillai, D. I. Prajapati, R. Ameta, and Y. Ali, "Preparation of C-TiO2 nanophotocatalyst and its used for degradation of evans blue," Sci Revs Chem Commun, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 12-18, 2016.
[18] I. Ben Amor, H. Hemmami, S. E. Laouini, M. S. Mahboub, and A. Barhoum, "Sol-Gel Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Different Chitosan Sources: Effects on Antibacterial Activity and Photocatalytic Degradation of AZO Dye," Catalysts, vol. 12, no. 12, p. 1611, 2022.
[19] A. A. Mariod and H. J. A. S. P. T. A. Fadul, "Gelatin, source, extraction and industrial applications," vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 135-147, 2013.
[20] N. Q. I. M. Noor et al., "Application of green technology in gelatin extraction: A review," vol. 9, no. 12, p. 2227, 2021.
[21] M. S. P. Abdullah et al., "Physicochemical evaluation and spectroscopic characterisation of gelatine from shank and toes of Gallus gallus domesticus," Sains Malaysiana, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 435-449, 2016.
[22] R. Gál, P. Mokrejš, P. Mrázek, J. Pavlačková, D. Janáčová, and J. Orsavová, "Chicken heads as a promising by-product for preparation of food gelatins," Molecules, vol. 25, no. 3, p. 494, 2020.
[23] A. K. Chakka, A. Muhammed, P. Sakhare, and N. Bhaskar, "Poultry processing waste as an alternative source for mammalian gelatin: Extraction and characterization of gelatin from chicken feet using food grade acids," Waste and Biomass Valorization, vol. 8, pp. 2583-2593, 2017.
[24] O. Aidat, L. Belkacemi, M. Belalia, M. khairi Zainol, and H. S. Barhoum, "Physicochemical, rheological, and textural properties of gelatin extracted from chicken by-products (feet-heads) blend and application," International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science, vol. 32, p. 100708, 2023.
[25] A. A. Karim, R. J. T. i. f. s. Bhat, and technology, "Gelatin alternatives for the food industry: recent developments, challenges and prospects," vol. 19, no. 12, pp. 644-656, 2008.
[26] J. Gómez-Estaca, M. Gómez-Guillén, F. Fernández-Martín, and P. J. F. H. Montero, "Effects of gelatin origin, bovine-hide and tuna-skin, on the properties of compound gelatin–chitosan films," vol. 25, no. 6, pp. 1461-1469, 2011.
[27] S. Anisuzzaman, C. G. Joseph, C. K. Pang, N. A. Affandi, S. N. Maruja, and V. Vijayan, "Current trends in the utilization of photolysis and photocatalysis treatment processes for the remediation of dye wastewater: A short review," ChemEngineering, vol. 6, no. 4, p. 58, 2022.
التنزيلات
منشور
إصدار
القسم
الفئات
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2025 Houssam Eddine Serouti, Choukri Ouaggadi, Dhia Eddine Megeurhi (Author)

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


