Preparation methods, properties of carbon quantum dots, and their advanced applications
Keywords:
Carbon Quantum Dots, Synthesis Methods, Optical Properties, Drug Delivery, Environmental ApplicationsAbstract
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) have emerged as a versatile class of nanomaterials due to their unique optical, chemical, and biological properties. This essay explores the synthesis methods of CQDs, categorized into top-down and bottom-up approaches, including techniques such as laser ablation, electrochemical synthesis, hydrothermal, and microwave irradiation methods. The optical properties, including absorbance, photoluminescence, and fluorescence, are discussed alongside their chemical inertness and adsorption capabilities. Advanced characterization techniques, such as mass spectrometry, spectroscopy, microscopy, and diffraction, are reviewed for their role in understanding CQD structure and functionality. The essay further delves into CQD applications in environmental monitoring, bioimaging, optoelectronics, and cancer treatment, with a focus on photodynamic therapy, photothermal therapy, and drug delivery. By highlighting their biocompatibility and tunable properties, this work underscores the transformative potential of CQDs in addressing critical challenges in healthcare and environmental sustainability.
Downloads
References
[1] B. Acharya, A. Behera, S. Behera, and S. J. I. C. C. Moharana, "Carbon quantum dots: A systematic overview of recent developments in synthesis, properties, and novel therapeutic applications," p. 112492, 2024.
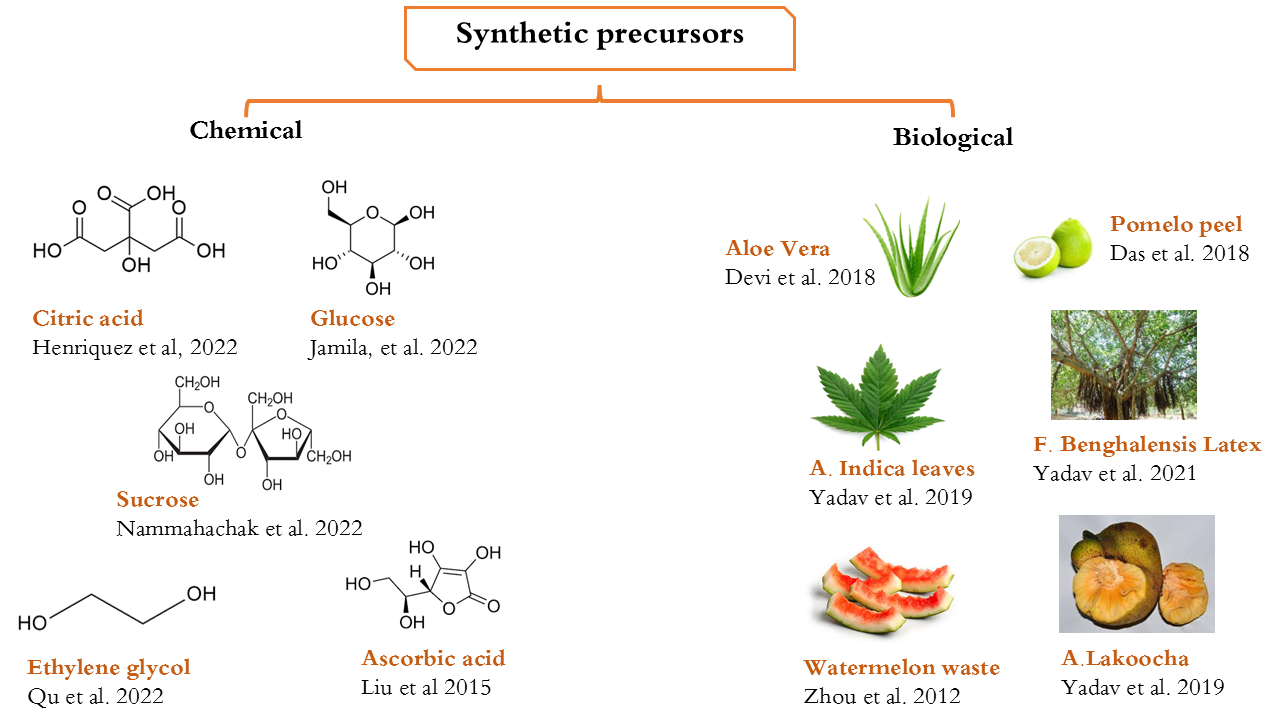
[2] R. Das, R. Bandyopadhyay, and P. J. M. t. c. Pramanik, "Carbon quantum dots from natural resource: A review," vol. 8, pp. 96-109, 2018.
[3] S. Palagati, J. J. A. M. P. Reddy, Characterization, and M. Applications, "Synthesis by Top-Down and Bottom-Up," p. 201, 2024.
[4] R. Wang, K.-Q. Lu, Z.-R. Tang, and Y.-J. J. J. o. M. C. A. Xu, "Recent progress in carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications in photocatalysis," vol. 5, no. 8, pp. 3717-3734, 2017.
[5] A. S. Rasal et al., "Carbon quantum dots for energy applications: a review," vol. 4, no. 7, pp. 6515-6541, 2021.
[6] M. J. J. S. E. Molaei, "The optical properties and solar energy conversion applications of carbon quantum dots: A review," vol. 196, pp. 549-566, 2020.
[7] H.-L. Yang et al., "Carbon quantum dots: Preparation, optical properties, and biomedical applications," vol. 18, p. 100376, 2023.
[8] A. M. O. R. Ben, H. E. M. M. A. M. I. Asma, G. H. E. R. B. I. Hadia, and M. Taher, "Synthesis of spherical carbon nanoparticles from orange peel and their surface modification with chitosan: evaluation of optical properties, biocompatibility, antioxidant and anti-hemolytic activity," Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, vol. 15, no. 7, pp. 11345–11358, 2025.
[9] D. L. Zhao and T.-S. J. W. r. Chung, "Applications of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) in membrane technologies: A review," vol. 147, pp. 43-49, 2018.
[10] P. K. Yadav, S. Chandra, V. Kumar, D. Kumar, and S. H. J. C. Hasan, "Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, structure, properties, and catalytic applications for organic synthesis," vol. 13, no. 2, p. 422, 2023.
[11] S. Paulo, E. Palomares, and E. Martinez-Ferrero, "Graphene and carbon quantum dot-based materials in photovoltaic devices: From synthesis to applications," Nanomaterials, vol. 6, no. 9, p. 157, 2016.
[12] F. Yuan, W. Su, and F. Gao, "Monolayer 2D polymeric fullerene: A new member of the carbon material family," Chem, vol. 8, no. 8, pp. 2079-2081, 2022.
[13] Y. Liu, H. Huang, W. Cao, B. Mao, Y. Liu, and Z. Kang, "Advances in carbon dots: from the perspective of traditional quantum dots," Materials Chemistry Frontiers, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1586-1613, 2020.
[14] H. Li et al., "Synthesis of carbon quantum dots for application of alleviating amyloid-β mediated neurotoxicity," Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, vol. 212, p. 112373, 2022.
[15] L. Cui, X. Ren, J. Wang, and M. Sun, "Synthesis of homogeneous carbon quantum dots by ultrafast dual-beam pulsed laser ablation for bioimaging," Materials Today Nano, vol. 12, p. 100091, 2020.
[16] C. Doñate-Buendía, M. Fernández-Alonso, J. Lancis, and G. Mínguez-Vega, "Pulsed laser ablation in liquids for the production of gold nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots: From plasmonic to fluorescence and cell labelling," in Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, vol. 1537, no. 1, p. 012013: IOP Publishing.
[17] Q.-L. Zhao, Z.-L. Zhang, B.-H. Huang, J. Peng, M. Zhang, and D.-W. Pang, "Facile preparation of low cytotoxicity fluorescent carbon nanocrystals by electrooxidation of graphite," Chemical Communications, no. 41, pp. 5116-5118, 2008.
[18] L. Zheng, Y. Chi, Y. Dong, J. Lin, and B. Wang, "Electrochemiluminescence of water-soluble carbon nanocrystals released electrochemically from graphite," Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 131, no. 13, pp. 4564-4565, 2009.
[19] J. Deng et al., "Electrochemical synthesis of carbon nanodots directly from alcohols," Chemistry–A European Journal, vol. 20, no. 17, pp. 4993-4999, 2014.
[20] Y. Hou, Q. Lu, J. Deng, H. Li, and Y. Zhang, "One-pot electrochemical synthesis of functionalized fluorescent carbon dots and their selective sensing for mercury ion," Analytica Chimica Acta, vol. 866, pp. 69-74, 2015.
[21] G. Sun, M. Y. Berezin, J. Fan, K. Zhang, S. Achilefu, and K. L. Wooley, "Optimizations of Quantum Yield of Fluorescent Nanoparticles for Development of Potential Optical Imaging Contrast Agents," Developing New Methodologies for Crosslinked Polymeric Nanostructure Syntheses, Chemoselective Modifications, and Applications as Imaging and Delivery Agents, p. 171, 2009.
[22] F. Chao-Mujica et al., "Carbon quantum dots by submerged arc discharge in water: Synthesis, characterization, and mechanism of formation," vol. 129, no. 16, 2021.
[23] L. Wang et al., "One step synthesis of Al/N co-doped carbon nanoparticles with enhanced photoluminescence," Journal of Luminescence, vol. 158, pp. 1-5, 2015.
[24] S. Inderbir, R. Arora, H. Dhiman, and R. Pahwa, "Carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, characterization and biomedical applications," Turk. J. Pharm. Sci, vol. 2, pp. 219–230, 2018.
[25] Y. Qu et al., "Controllable synthesis of a sponge-like Z-scheme N, S-CQDs/Bi2MoO6@ TiO2 film with enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity under visi-ble/NIR light irradiation," J. Hazard. Mater, vol. 429, p. 128310, 2022.
[26] C. Kaixin, Q. Zhu, L. Qi, M. Guo, W. Gao, and Q. Gao, "Synthesis and Properties of Nitro-gen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Using Lactic Acid as Carbon Source," Materials, vol. 15, p. 466, 2022.
[27] G. Henriquez, J. Ahlawat, R. Fairman, and M. Narayan, "Citric Acid-Derived Carbon Quantum Dots Attenuate Paraquat-Induced Neuronal Compromise In Vitro and In Vivo," ACS Chem. Neurosci, vol. 13, pp. 2399–2409, 2022.
[28] G. S. Jamila, S. Sajjad, S. A. K. Leghari, T. Kallio, and C. Flox, "Glucose derived carbon quantum dots on tungstate-titanate nanocomposite for hydrogen energy evolution and solar light catalysis," J. Nanostruct. Chem, vol. 12, pp. 611–623, 2021.
[29] Y. Qiu, D. Li, Y. Li, X. Ma, and J. Li, "Green carbon quantum dots from sustainable lignocellulosic biomass and its application in the detection of Fe3+," Cellulose, vol. 29, pp. 367–378, 2021.
[30] H. M. E. M. El-Brolsy, N. A. N. Hanafy, and M. A. El-Kemary, "Fighting Non-Small Lung Cancer Cells Using Optimal Functionalization of Targeted Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Natural Sources Might Provide Potential Therapeutic and Cancer Bio Image Strategies," Int. J. Mol. Sci, vol. 23, p. 13283, 2022.
[31] L. Yao et al., "Carbon Quantum Dots-Based Nanozyme from Coffee Induces Cancer Cell Ferroptosis to Activate Antitumor Immunity," ACS Nano, vol. 16, pp. 9228–9239, 2022.
[32] M. Kumari, G. R. Chaudhary, S. Chaudhary, A. Umar, S. Akbar, and S. Baskoutas, "Bio-Derived Fluorescent Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications," Molecules, vol. 27, p. 5329, 2022.
[33] B. Zhang, C. Liu, and Y. Liu, "A Novel One-Step Approach to Synthesize Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles," Eur. J. Inorg. Chem, pp. 4411–4414, 2010.
[34] H. U. Castañeda-Serna, G. Calderón-Domínguez, A. García-Bórquez, M. Salgado-Cruz, and R. R. F. Rebollo, "Structural and luminescent properties of CQDs produced by microwave and conventional hy-drothermal methods using pelagic Sargassum as carbon source," Opt. Mater, vol. 126, p. 112156, 2022.
[35] X. Huo, L. Liu, Y. Bai, J. Qin, L. Yuan, and F. Feng, "Facile synthesis of yellowish-green emitting carbon quantum dots and their applications for phoxim sensing and cellular imaging," Anal. Chim. Acta, p. 338685, 2021.
[36] H. Ye, B. Liu, J. Wang, C. Zhou, Z. Xiong, and L. Zhao, "A Hydrothermal Method to Generate Carbon Quantum Dots from Waste Bones and Their Detection of Laundry Powder," Molecules, vol. 27, p. 6479, 2022.
[37] G. S. Jamila, S. Sajjad, S. A. K. Leghari, T. Kallio, and C. Flox, "Glucose derived carbon quantum dots on tungstate-titanate nanocomposite for hydrogen energy evolution and solar light catalysis," Journal of Nanostructure in Chemistry, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 611-623, 2022.
[38] N. Nammahachak et al., "Hydrothermal synthesis of carbon quantum dots with size tunability via heterogeneous nucleation," RSC advances, vol. 12, no. 49, pp. 31729-31733, 2022.
[39] G. Henriquez, J. Ahlawat, R. Fairman, and M. Narayan, "Citric acid-derived carbon quantum dots attenuate paraquat-induced neuronal compromise in vitro and in vivo," ACS Chemical Neuroscience, vol. 13, no. 16, pp. 2399-2409, 2022.
[40] R. Liu, D. Wu, S. Liu, K. Koynov, W. Knoll, and Q. Li, "An Aqueous Route to Multicolor Photoluminescent Carbon Dots Using Silica Spheres as Carriers," Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, vol. 48, pp. 4598–4601, 2009.
[41] R. Liu, D. Wu, S. Liu, K. Koynov, W. Knoll, and Q. Li, "An aqueous route to multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots using silica spheres as carriers," Angewandte Chemie International Edition, vol. 48, no. 25, pp. 4598-4601, 2009.
[42] D. Pan, J. Zhang, Z. Li, C. Wu, X. Yan, and M. Wu, "Observation of pH-, solvent-, spin-, and excitation-dependent blue photoluminescence from carbon nanoparticles," Chemical Communications, vol. 46, no. 21, pp. 3681-3683, 2010.
[43] B. C. Martindale, G. A. Hutton, C. A. Caputo, and E. Reisner, "Solar hydrogen production using carbon quantum dots and a molecular nickel catalyst," Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 137, no. 18, pp. 6018-6025, 2015.
[44] M. Rong, Y. Feng, Y. Wang, and X. Chen, "One-pot solid phase pyrolysis synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots for Fe3+ sensing and bioimaging," Sens. Actuators B Chem, vol. 245, pp. 868–874, 2017.
[45] M. Otten, M. Hildebrandt, R. Kühnemuth, and M. Karg, "Pyrolysis and solvothermal synthesis for carbon dots: role of purification and molecular fluorophores," Langmuir, vol. 38, no. 19, pp. 6148-6157, 2022.
[46] H. Zhu, X. Wang, Y. Li, Z. Wang, F. Yang, and X. Yang, "Microwave synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles with electrochemiluminescence properties," Chemical Communications, no. 34, pp. 5118-5120, 2009.
[47] K. Krishnamoorthy, M. Veerapandian, R. Mohan, and S.-J. Kim, "Investigation of Raman and photoluminescence studies of reduced graphene oxide sheets," Applied Physics A, vol. 106, pp. 501-506, 2012.
[48] P. K. Bebas, M. A. Larsson, P. Ramachandran, P. Jarujamrus, and H. L. Lee, "Microwave synthesis of blue emissive N-doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for free chlorine detection," Sains Malays, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 1197-1212, 2022.
[49] H. Laddha et al., "One-pot microwave-assisted synthesis of blue emissive multifunctional NSP co-doped carbon dots as a nanoprobe for sequential detection of Cr (VI) and ascorbic acid in real samples, fluorescent ink and logic gate operation," Journal of molecular liquids, vol. 346, p. 117088, 2022.
[50] A. Ahlawat, P. S. Rana, and P. R. Solanki, "Studies of photocatalytic and optoelectronic properties of microwave synthesized and polyethyleneimine stabilized carbon quantum dots," Materials Letters, vol. 305, p. 130830, 2021.
[51] A. B. Bourlinos, A. Stassinopoulos, D. Anglos, R. Zboril, V. Georgakilas, and E. P. Giannelis, "Photoluminescent carbogenic dots," Chemistry of Materials, vol. 20, no. 14, pp. 4539-4541, 2008.
[52] C. Hu et al., "Chemically tailoring coal to fluorescent carbon dots with tuned size and their capacity for Cu (II) detection," vol. 10, no. 23, pp. 4926-4933, 2014.
[53] S. Wang, K. Kirillova, and X. Lehto, "Travelers’ food experience sharing on social network sites," J. Travel Tour. Mark, vol. 34, pp. 680–693, 2016.
[54] S. Anwar et al., "Recent advances in synthesis, optical properties, and bio-medical applications of carbon dots," ACS Appl. Bio Mater, vol. 6, pp. 2317–2338, 2019.
[55] M. A. Jhonsi, "Carbon Quantum Dots for Bioimaging," in State of the Art in Nano-Bioimaging; IntechOpenLondon, UK, 2018, pp. 35–55.
[56] L. Li and T. Dong, "Photoluminescence tuning in carbon dots: Surface passivation or/and functionalization, heteroatom doping," J. Mater. Chem. C, vol. 30, pp. 7944–7970, 2018.
[57] H. Peng and J. Travas-Sejdic, "Simple Aqueous Solution Route to Luminescent Carbogenic Dots from Carbohydrates," Chem. Mater, vol. 21, pp. 5563–5565, 2009.
[58] L. Wang et al., "Full-color fluorescent carbon quantum dots," Sci. Adv, vol. 6, p. 6772, 2020.
[59] C. Darragh, C. Rocks, D. B. Padmanaban, P. Maguire, V. Svrcek, and D. Mariotti, "Environmentally friendly nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for next generation solar cells," Sustain. Energy Fuels, vol. 7, pp. 1611–1619, 2017.
[60] R. Gao et al., "Green Preparation of Fluorescent Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Sensitive Detection of Oxytetracycline in Environmental Samples," Nanomaterials, vol. 10, p. 1561, 2020.
[61] J. Yu et al., "Luminescence Mechanism of Carbon Dots by Tailoring Functional Groups for Sensing Fe3+ Ions," Nanomaterials, vol. 8, p. 233, 2018.
[62] G. Zuo, A. Xie, J. Li, T. Su, X. Pan, and W. Dong, "Large Emission Red-Shift of Carbon Dots by Fluorine Doping and Their Applications for Red Cell Imaging and Sensitive Intracellular Ag+ Detection," J. Phys. Chem. C, vol. 121, pp. 26558–26565, 2017.
[63] K. J. Mintz, Y. Zhou, and R. M. J. N. Leblanc, "Recent development of carbon quantum dots regarding their optical properties, photoluminescence mechanism, and core structure," vol. 11, no. 11, pp. 4634-4652, 2019.
[64] E. Caluwé, K. Halamouá, P. Damme, and L. Adansoniadigitata, "A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology," Afr. Focus, vol. 1, pp. 11–51, 2010.
[65] C. Lu, Q. Su, and X. Yang, "Ultra-long room-temperature phosphorescent carbon dots: pH sensing and dualchannel detection of tetracyclines," Nanoscale, vol. 11, pp. 16036–16042, 2019.
[66] S. Tao, S. Zhu, T. Feng, C. Xia, Y. Song, and B. J. M. t. c. Yang, "The polymeric characteristics and photoluminescence mechanism in polymer carbon dots: A review," vol. 6, pp. 13-25, 2017.
[67] M. Jorns and D. J. N. Pappas, "A review of fluorescent carbon dots, their synthesis, physical and chemical characteristics, and applications," vol. 11, no. 6, p. 1448, 2021.
[68] Q. Zhang, R. Wang, B. Feng, X. Zhong, and K. Ostrikov, "Photoluminescence mechanism of carbon dots: Triggering high-color-purity red fluorescence emission through edge amino protonation," Nat. Commun, vol. 12, p. 6856, 2021.
[69] Y. An et al., "Preparation of Multicolour Solid Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Light-Emitting Diodes Using Phenylethylamine as a Co-Carbonization Agent," Int. J. Mol. Sci, vol. 23, p. 11071, 2022.
[70] J. Shen, Y. Zhu, C. Chen, X. Yang, and C. Li, "Facile preparation and upconversionlumi-nescence of graphene quantum dots," Chem. Commun, vol. 9, pp. 2580–2582, 2011.
[71] A. Nourbakhsh et al., "Bandgap opening in oxygen plasma-treated graphene," Nanotechnology, vol. 21, p. 435203, 2010.
[72] M. O. Dekaliuk, O. Viagin, Y. V. Malyukin, and A. P. Demchenko, "Fluorescent carbon nanomateri-als:“Quantum dots” or nanoclusters?," Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys, vol. 30, pp. 16075–16084, 2014.
[73] D. Bibekananda and N. Karak, "A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice," RSC Adv, vol. 22, pp. 8286–8290, 2013.
[74] B. Zhi, X. Yao, Y. Cui, G. Orr, and C. L. Haynes, "Synthesis, applications and potential photoluminescence mechanism of spectrally tunable carbon dots," Nanoscale, vol. 11, pp. 20411–20428, 2019.
[75] Y. Sun, M. Zhang, B. Bhandari, and C. J. F. R. I. Yang, "Recent development of carbon quantum dots: biological toxicity, antibacterial properties and application in foods," vol. 38, no. 7, pp. 1513-1532, 2022.
[76] K. Tungare, M. Bhori, K. S. Racherla, and S. J. B. Sawant, "Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility studies of carbon quantum dots from Phoenix dactylifera," vol. 10, no. 12, p. 540, 2020.
[77] S.-T. Yang et al., "Carbon dots as nontoxic and high-performance fluorescence imaging agents," vol. 113, no. 42, pp. 18110-18114, 2009.
[78] Y. Wang et al., "Carbon dots of different composition and surface functionalization: cytotoxicity issues relevant to fluorescence cell imaging," vol. 236, no. 11, pp. 1231-1238, 2011.
[79] A. Cruz-Cruz et al., "Recent advances in carbon dots based biocatalysts for degrading organic pollutants," vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 384-394, 2022.
[80] J. Liu et al., "One-step hydrothermal synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots with selective antibacterial activity against Porphyromonas gingivalis," vol. 9, no. 21, pp. 7135-7142, 2017.
[81] K. Wang et al., "N-doped carbon dots as robust fluorescent probes for the rapid detection of hypochlorite," vol. 12, no. 42, pp. 27170-27178, 2022.
[82] X. Wang, Y. Feng, P. Dong, and J. J. F. i. c. Huang, "A mini review on carbon quantum dots: preparation, properties, and electrocatalytic application," vol. 7, p. 671, 2019.
[83] Q. Hu, X. Gong, L. Liu, and M. M. F. Choi, "Characterization and analytical separation of fluorescent carbon nanodots," J. Nanomater, pp. 30–37, 2017.
[84] Q. Hu, X. Meng, and W. Chan, "An investigation on the chemical structure of nitrogen and sulfur codoped carbon nanoparticles by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry," Anal. Bioanal. Chem, vol. 408, pp. 5347–5357, 2016.
[85] Q. Hu, X. Meng, M. M. F. Choi, X. Gong, and W. Chan, "Elucidating the structure of carbon nanoparticles by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionisation quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry," Anal. Chim. Acta, vol. 911, pp. 100–107, 2016.
[86] Q. Hu et al., "Better understanding of carbon nanoparticles via high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection and mass spectrometry," Electrophoresis, vol. 35, pp. 2454–2462, 2014.
[87] Q. Hu, X. Gong, L. Liu, and M. M. J. J. o. N. Choi, "Characterization and analytical separation of fluorescent carbon nanodots," vol. 2017, no. 1, p. 1804178, 2017.
[88] A. Dager, T. Uchida, T. Maekawa, and M. Tachibana, "Synthesis and characterization of mono-disperse carbon quantum dots from fennel seeds: Photoluminescence analysis using machine learning," Sci. Rep, vol. 9, pp. 1–10, 2019.
[89] L. C. Sim et al., "Carbon dots synthesized from green precursors with an amplified photoluminescence: Synthesis, characterization, and its application," in Plant NanobionicsCham, Switzerland: Springer, 2019.
[90] D. Houdová et al., "Chemically heterogeneous carbon dots enhanced cholesterol detection by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry," Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, vol. 591, pp. 373-383, 2021.
[91] D. Nagarajan, O. M. Varada, and S. Venkatanarasimhan, "Carbon dots coated on amine functionalized cellulose sponge for the adsorption of the toxic herbicide atrazine," Mater. Today Proc, 2020.
[92] S. Demirci, A. B. McNally, R. S. Ayyala, L. B. Lawson, and N. Sahiner, "Synthesis and characterization of nitrogen-doped carbon dots as fluorescent nanoprobes with antimicrobial properties and skin permeability," J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol, vol. 59, p. 101889, 2020.
[93] M. Zaib, A. Akhtar, F. Maqsood, T. J. A. J. f. S. Shahzadi, and Engineering, "Green synthesis of carbon dots and their application as photocatalyst in dye degradation studies," vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 437-446, 2021.
[94] C. M. Carbonaro et al., "On the emission properties of carbon dots: reviewing data and discussing models," vol. 5, no. 4, p. 60, 2019.
[95] A. Mewada et al., "Green synthesis of biocompatible carbon dots using aqueous extract of Trapa bispinosa peel," vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 2914-2917, 2013.
[96] B. De and N. J. R. A. Karak, "A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice," vol. 3, no. 22, pp. 8286-8290, 2013.
[97] B. Demir et al., "Carbon dots and curcumin-loaded CD44-Targeted liposomes for imaging and tracking cancer chemotherapy: A multi-purpose tool for theranostics," Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, vol. 62, p. 102363, 2021.
[98] O. Rojas-Valencia, M. Regules-Carrasco, J. Hernández-Fuentes, C. Reza-San Germán, M. Estrada-Flores, and E. Villagarcía-Chávez, "Synthesis of blue emissive carbon quantum dots from Hibiscus Sabdariffa flower: Surface functionalization analysis by FT-IR spectroscopy," Materialia, vol. 19, p. 101182, 2021.
[99] M. Yahaya Pudza, Z. Zainal Abidin, S. Abdul Rashid, F. Md Yasin, A. Noor, and M. A. Issa, "Eco-friendly sustainable fluorescent carbon dots for the adsorption of heavy metal ions in aqueous environment," Nanomaterials, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 315, 2020.
[100] M. A. Haruna, Z. Hu, H. Gao, J. Gardy, S. M. Magami, and D. Wen, "Influence of carbon quantum dots on the viscosity reduction of polyacrylamide solution," Fuel, vol. 248, pp. 205-214, 2019.
[101] R. Gao et al., "Green preparation of fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for sensitive detection of oxytetracycline in environmental samples," Nanomaterials, vol. 10, no. 8, p. 1561, 2020.
[102] J. J. Pesek and M. T. Matyska, "Spectroscopic characterization of chemically modified oxide surfaces," Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal, vol. 120 A, pp. 117–142, 1999.
[103] Q. Li, T. Zhang, Y. Pan, L. C. Ciacchi, B. Xu, and G. Wei, "AFM-based force spectroscopy for bioimaging and biosensing," RSC Adv. 2016, vol. 6, pp. 12893–12912.
[104] J. J. Huang, Z. F. Zhong, M. Z. Rong, X. Zhou, X. D. Chen, and M. Q. Zhang, "An easy approach of preparing strongly luminescent carbon dots and their polymer based composites for enhancing solar cell efficiency," Carbon N. Y, vol. 70, pp. 190–198, 2014.
[105] W. Chen, C. Hu, Y. Yang, J. Cui, and Y. Liu, "Rapid synthesis of carbon dots by hydrothermal treatment of lignin," Materials, p. 9, 2016.
[106] Q. Wang, S. Zhang, H. Ge, G. Tian, N. Cao, and Y. Li, "A fluorescent turn-off/on method based on carbon dots as fluorescent probes for the sensitive determination of Pb2+ and pyrophosphate in an aqueous solution," Sensors Actuators, B Chem, vol. 207, pp. 25–33, 2015.
[107] A. F. Shaikh, M. S. Tamboli, R. H. Patil, A. Bhan, J. D. Ambekar, and B. B. Kale, "Bioinspired carbon quantum dots: an antibiofilm agents," Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 2339-2345, 2019.
[108] Y. Lou et al., "Recent advances of biomass carbon dots on syntheses, characterization, luminescence mechanism, and sensing applications," Nano Select, vol. 2, no. 6, pp. 1117-1145, 2021.
[109] N. Kazemifard, A. A. Ensafi, and B. Rezaei, "Green synthesized carbon dots embedded in silica molecularly imprinted polymers, characterization and application as a rapid and selective fluorimetric sensor for determination of thiabendazole in juices," Food Chem, vol. 310, p. 125812, 2020.
[110] L. Zhou, Y. Lin, Z. Huang, J. Ren, and X. Qu, "Carbon nanodots as fluorescence probes for rapid, sensitive, and label-free detection of Hg2+ and biothiols in complex matrices," Chem. Commun, vol. 48, pp. 1147–1149, 2012.
[111] N. Arumugam and J. Kim, "Synthesis of carbon quantum dots from Broccoli and their ability to detect silver ions," Mater. Lett, vol. 219, pp. 37–40, 2018.
[112] G. H. Liu et al., "High-fluorescent carbon dots (CDs) originated from China grass carp scales (CGCS) for effective detection of Hg(II) ions," Microchem. J, vol. 145, pp. 718–728, 2019.
[113] S. C. Pandey, A. Kumar, and S. K. Sahu, "Single Step Green Synthesis of Carbon Dots from Murraya koenigii leaves; A Unique Turn-off Fluorescent contrivance for Selective Sensing of Cd (II) ion," J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem, vol. 400, p. 112620, 2020.
[114] Y. B. Su, B. Yu, S. Wang, H. L. Cong, and Y. Q. Shen, "NIR-II bioimaging of small organic molecule," Biomaterials, vol. 271, p. 120717, 2021.
[115] A. B. Bourlinos, A. Stassinopoulos, D. Anglos, R. Zboril, M. Karakassides, and E. P. Giannelis, "Surface functionalized carbogenic quantum dots," Small, vol. 4, pp. 455–458, 2008.
[116] S. J. Zhu et al., "Highly Photoluminescent Carbon Dots for Multicolor Patterning, Sensors, and Bioimaging," Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, vol. 52, pp. 3953–3957, 2013.
[117] C. X. Huang, H. L. Dong, Y. Su, Y. Wu, R. Narron, and Q. Yong, "Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dot Nanoparticles Derived from Byproducts in Bio-Refinery Process for Cell Imaging and In Vivo Bioimaging," Nanomaterials, vol. 9, p. 387, 2019.
[118] P. Mirtchev, E. J. Henderson, N. Soheilnia, C. M. Yip, and G. A. Ozin, "Solution phase synthesis of carbon quantum dots as sensitizers for nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells," J. Mater. Chem, vol. 22, pp. 1265–1269, 2012.
[119] Y. Q. Zhang, D. K. Ma, Y. G. Zhang, W. Chen, and S. M. Huang, "N-doped carbon quantum dots for TiO2-based photocatalysts and dye-sensitized solar cells," Nano Energy, vol. 2, pp. 545–552, 2013.
[120] H. Y. Xiong et al., "The preparation of carbon dots/ionic liquids-based electrolytes and their applications in quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells," Electrochim. Acta, vol. 88, pp. 100–106, 2013.
[121] C. Shen, J. Wang, Y. Cao, and Y. Lu, "Facile access to B-doped solid-state fluorescent carbon dots toward light emitting devices and cell imaging agents," J. Mater. Chem. C, vol. 3, pp. 6668–6675, 2015.
[122] Q. M. Yang, W. Yang, Y. Zhang, W. Ge, X. Yang, and P. Z. Yang, "Precise Surface State Control of Carbon Quantum Dots to Enhance Charge Extraction for Solar Cells," Nanomaterials, vol. 10, p. 460, 2020.
[123] X. Han, S. Zhong, W. Pan, and W. J. N. Shen, "A simple strategy for synthesizing highly luminescent carbon nanodots and application as effective down-shifting layers," vol. 26, no. 6, p. 065402, 2015.
[124] H. Ding, X. X. Zhou, B. T. Qin, Z. Y. Zhou, and Y. P. Zhao, "Highly fluorescent near-infrared emitting carbon dots derived from lemon juice and its bioimaging application," J. Lumin, vol. 211, pp. 298–304, 2019.
[125] J. Ferlay et al., "Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview," Int. J. Cancer, vol. 149, pp. 778–789, 2021.
[126] M. A. Ansari et al., "Nanozymes and carbon-dots based nanoplatforms for cancer imaging, diagnosis and therapeutics: Current trends and challenges," Environ. Res, vol. 241, p. 117522, 2023.
[127] S. Bayda, E. Amadio, S. Cailotto, Y. Frión-Herrera, A. Perosa, and F. Rizzolio, "Carbon dots for cancer nanomedicine: A bright future," Nanoscale Adv, vol. 3, pp. 5183–5221, 2021.
[128] X. S. Li, J. F. Lovell, J. Yoon, and X. Y. Chen, "Clinical development and potential of photothermal and photodynamic therapies for cancer," Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol, vol. 17, pp. 657–674, 2020.
[129] S. Chen, T. T. Sun, M. Zheng, and Z. G. Xie, "Carbon Dots Based Nanoscale Covalent Organic Frameworks for Photodynamic Therapy," Adv. Funct. Mater, vol. 30, p. 2004680, 2020.
[130] M. Zheng, Y. Li, S. Liu, W. Q. Wang, Z. G. Xie, and X. B. Jing, "One-Pot To Synthesize Multifunctional Carbon Dots for Near Infrared Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal Cancer Therapy," ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 8, pp. 23533–23541, 2016.
[131] X. Bao et al., "In vivo theranostics with near-infraredemitting carbon dots—Highly efficient photothermal therapy based on passive targeting after intravenous administration," Light Sci. Appl, vol. 7, p. 91, 2018.
[132] A. B. Amor et al., "Advances in carbon quantum dot applications: catalysis, sensing, and biomedical innovations," vol. 185, p. 108945, 2025.
[133] T. Kong, L. Hao, Y. Wei, X. Cai, and B. Zhu, "Doxorubicin conjugated carbon dots as a drug delivery system for human breast cancer therapy," Cell proliferation, vol. 51, no. 5, p. e12488, 2018.
[134] T. Feng, X. Ai, G. An, P. Yang, and Y. Zhao, "Charge-convertible carbon dots for imaging-guided drug delivery with enhanced in vivo cancer therapeutic efficiency," ACS nano, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 4410-4420, 2016.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Asma Ben Amor (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


